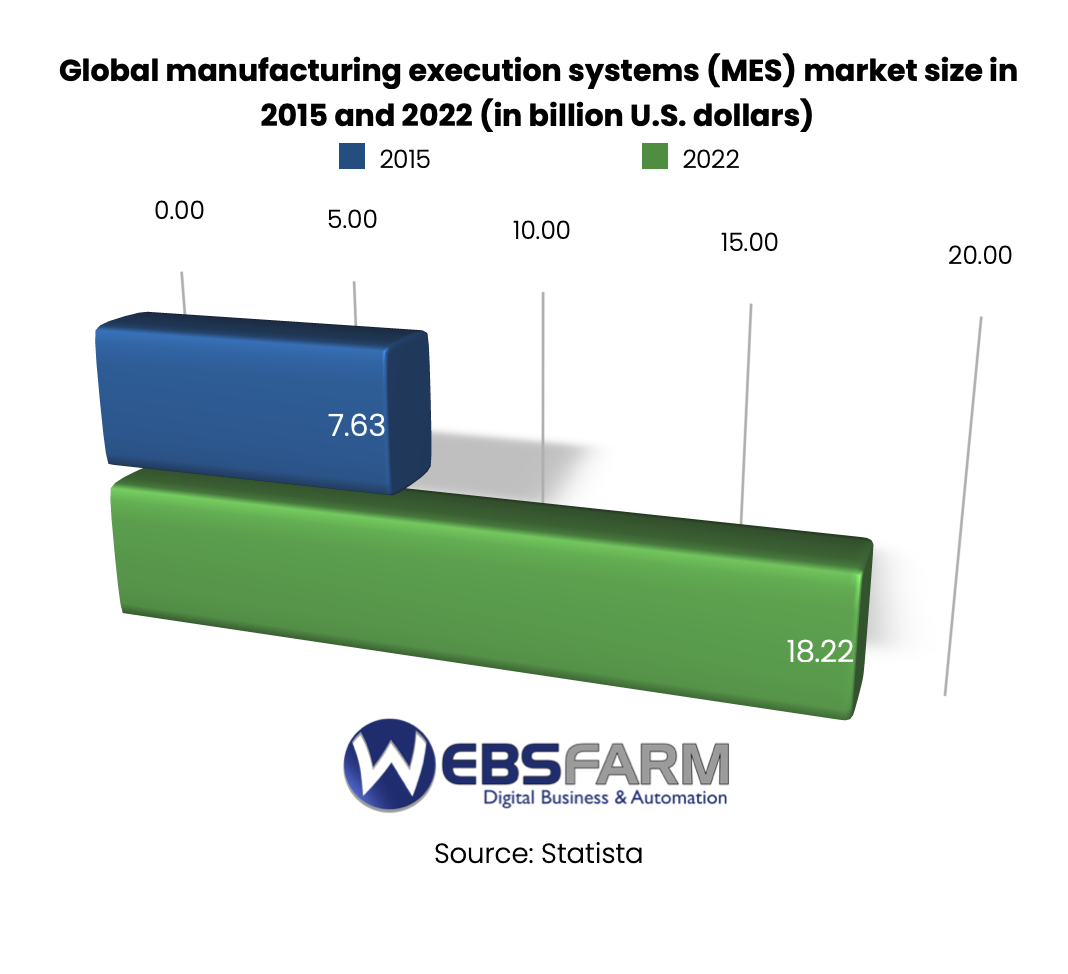
What is an MES System and Why Does It Matter?
How do manufacturers in today’s competitive marketplace improve efficiency to gain a competitive advantage? A manufacturing execution system (MES) can help you make more with less and ultimately, give your business its competitive edge.
But first, what exactly is a manufacturing execution system?
What is a manufacturing execution system (MES)?
The main goal of an MES system is to ensure the successful operation of manufacturing operations and to improve production efficiency. In essence, it’s an information system that connects, oversees and regulates complex manufacturing systems and data flows on the factory floor.
An MES helps achieve production goals by tracking and gathering precise, real-time data about the complete production lifecycle, beginning with order release until the product delivery stage for finished goods.
What are the benefits of a manufacturing execution system?
An MES is often integrated with key IT systems like ERP, supply chain management, product lifestyle management and more. Key benefits of using MES include:
- Heightened customer satisfaction
- Augmented regulatory compliance
- Superior agility and time to market
- Improved supply chain visibility
- Decreased manufacturing cycle time
- Elimination of paperwork and manual data-entry processes
- Reduced-order lead time
- Shortened labour costs
- Reduced WIP inventory
- Increased machine utilisation
What does MES do?
Below, we’ll take a look at the original MES core functions and how they’re used to improve manufacturing efficiency.
- 1. Operations management: Gives your employees a global view of planned production orders and their routing. This ensures that your whole staff is aligned around a unified production goal.
- 2. Dispatching production units: Manage the flow of production data in real-time between the ERP and the workshop ensuring that production data is always accurate, consistent and recent.
- 3. Product tracking & genealogy: Groups batches with corresponding manufacturing data. This data is of high importance to manufacturers that must comply with government or industry regulations.
- 4. Labour management: Easily manage people, products and operations and track any authorisations or skills that they require. This ensures you always have the right people with the right skillset in place at every step of the production process.
- 5. Quality management: Manage the quality of your manufacturing process and units—including quality deviations and exceptions.
- 6. Maintenance management: Plan preventative machine maintenance more easily to reduce downtime and production interruptions.
- 7. Data collection and acquisition: Track and gather crucial data and easily recover that data when you need it.
- 8. Process management: Provide process routing and operational sequencing—including full production traceability.
- 9. Performance analysis: Consolidate data to calculate key performance indicators (KPIs). This lets you know how your production process is working and how it could be improved.
- Document control: Provide a straightforward way for your operators to access important documents—including instructions, drawings, notes, and more. This saves you and your employees precious time by not having to search for physical documents.
- Resource allocation and status: Define and track the status of your resources and how they are used in the production process.
MES and Lean Principles
Many firms have adopted Lean Manufacturing as a means of increasing productivity and reducing cost, often by focusing on the implementation of Lean best practices to identify and eliminate waste. More specifically, the Lean approach aims to create processes that will necessitate less human effort, less space, less capital and less time to create and manufacture the product to make products and services less expensive and with fewer defects (compared to a traditional organisation).
The application of manufacturing execution systems can support the waste identification and elimination process essential to upholding Lean principles. The majority of MES vendors have now incorporated Lean functionality in their software, enabling them to boost production capacity and efficiency.
To implement an effective Lean approach, there is a need for reliable data that is properly collected and measured. That’s why an MES tool is so important: because manual data collection is ineffective. The frequency of data collection permitted by an MES tool will increase production efficiency and help solve problems quickly.
MES and ERP
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) system are powerful and strategic business process management tools that integrate all facets of an enterprise into one comprehensive information system that can be accessed by individuals across an entire organisation.
MES systems and ERP systems play separate but complementary roles in manufacturing operations. While ERP systems integrate all facets of an enterprise into one comprehensive information system, an MES acts as the layer between your manufacturing shop floor systems—like machines and supervisory systems—and your business, planning, and logistics systems. In sum, MES and ERP integrate to provide a single source of truth throughout your organisation.
MES and Automation
As mentioned, an MES facilitates the free-flow of information from the MES to the ERP and from the MES to the automation systems.
ERP, MES systems and equipment automation systems must work together seamlessly; one system’s output becomes another system’s input, and together, the manufacturing process becomes more scalable, predictable, reliable, and visible.